Microsoft SQL
Server is an application used to create
computer databases for the Microsoft Windows family of server operating systems.
It provides an environment used to generate databases that can be
accessed from workstations, the web, or other
media such as a personal digital assistant (PDA).
|
We will provide lessons and other topics on how to
use Microsoft SQL Server 2008.
In order to follow the lessons on this site, you
must have
access to a computer in which
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 is installed. To start, you
must have a computer that runs an appropriate operating system. If you
are just
learning, which is assumed for all lessons on this site, you can use a
Microsoft
Windows XP Professional, Microsoft Windows Vista, or Microsoft Windows Server 2003.
To use Microsoft SQL Server, you must install it on a
computer. You can install it on Microsoft Windows XP Professional,
Microsoft
Windows Vista, Microsoft Windows Server 2003, or Microsoft Windows
Server 2008.
This means that you should take care of the operating system first.
Before installing Microsoft SQL Server 2008, make
sure you
have installed all service packs on your operating system. If you plan
to use
Microsoft Visual Studio 2008 to create Microsoft SQL Server 2008
databases, you
should install Microsoft SQL Server 2008 first, then install Microsoft
Visual
Studio 2008.
One of the main concerns of a database is security,
and this is central to Microsoft SQL Server. Security is exercised at
different levels: in the room where the computer(s) is(are) located (the
computer(s) that hold the server application (Microsoft SQL Server) and
the computer(s) that will use(s) the databases (clients)) and the
people who will use all these resources.
When it comes to the room that houses the computer
on which
you will install Microsoft SQL Server, you should make sure the room can
be
locked at any time and only a few selected people have access to it. For
maximum
security, you should also put the computer in a locked closet.
|
Creating an Administrator Account |
|
To actually install Microsoft SQL Server 2008, you
must use
a user account that has the ability to install it. If you are using
Microsoft
Windows XP or Vista, you
should use the Administrator account or create a new
account that has administrative rights. The account you will use must
also
use/have a password. In Microsoft Windows XP Professional or Vista, to
use the
Administrator account, assign a password. Alternatively, after logging
in as
Administrator, create an account that has administrative rights.
|
 Practical
Learning: Creating an Account in MS Wnd XP or Vista Practical
Learning: Creating an Account in MS Wnd XP or Vista
|
|
- Start Control Panel and click User
Accounts:
![Control Panel]()
- Click Create New User:
![User Accounts]()
- Type the name for the new account as pkatts:
![User Accounts]()
- Click Next.
Make sure the Computer Administrator radio button is selected
![User Accounts]()
- Click Create Account
- To assign a password to an account, in the User Account,
click the pkatts account
- Click Create A Password
![User Accounts]()
- In the Type A New Password text box, type Password1 and
press
Tab
- Type Password1 to confirm and type anything in the last
text
box:
![User Accounts]()
- Click Create Password
- In the same way, create another account named gmonay
that has
administrative rights with the password Password1
|
 Practical
Learning: Creating an Account in a Server Practical
Learning: Creating an Account in a Server
|
|
- Log in to Microsoft Windows Server 2003 or 3008 with an account
that can
create an administrative account
- To create an account in Microsoft Windows Server 2003 or 2008, on
the taskbar, you can click Start -> Administrative Tools -> Active
Directory Users and
Computers
- In the left frame, right-click Users -> New User
![Active Directory Users and Computers]()
- Set the First Name as Patricia, the Initials as G,
the Last
Name as Katts, and the User Logon Name as pkatts (the
domain
name will be different from yours)
![New User]()
- Click Next
- Type the Password as Password1
- Type the Confirm Password as Password1 and accept the
options in
the check boxes
![New User]()
- Click Next (in the summary, the domain name will be different from
yours)
![New User]()
- Accept the options in the last page of the wizard and click Finish
- In the same way, create another account with the following
information:
First Name: Gertrude
LastName: Monay
User Logon Name: gmonay
Password: Password1
A security principal is a person or an object that
needs access to a database. The security principal can be considered as
one entity or as a group of entities:
![Security Principals]()
This means that a security principal can be
considered as a lone entity or as
part of a group. For example, a person who accesses a database can be
considered an entity. A group of people who exercise the same function
and have been give the same function(s) on a database is considered a
collection.
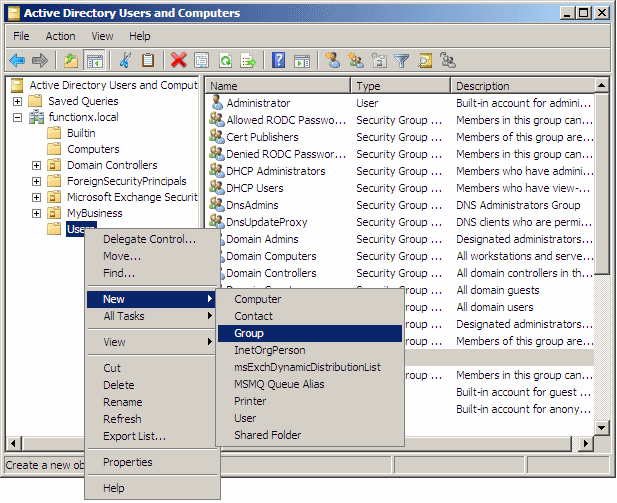
To create a group in Microsoft Windows Server 2003
or 2008,
open the Active Directory Users and Computers. Right-click the Users
node ->
New -> Group:
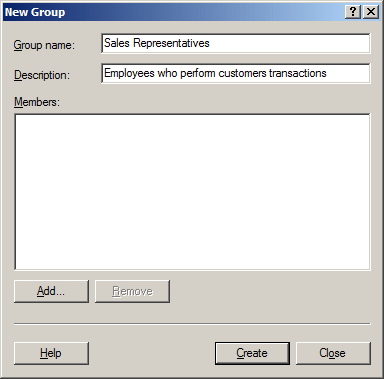
In the New Object - Group dialog box, give a name to
the new
group. Make the necessary selections in the Group Scope and the Group
Type:
When you have finished, click OK. After creating a
group,
you can use it. To use a group, you can add one or more existing users
to it. To
do this, locate the group and double-click it or right-click the group
and click Properties:

Add the necessary information.
To control the type of access that a security
principal can exercise on a machine or a database, it works or acts on a
level. There are three levels: Windows, server, and database:
![Security]()
Based on the functionality of a security principal,
it can be considered as belonging to a collection.
To help the operating system identify them, each
security principal uses a unique number called a security identifier
(SID).
|
 Practical
Learning: Adding an Account to a Group Practical
Learning: Adding an Account to a Group
|
|
- In the left frame, click Users if necessary.
In the right-click frame, double-click Domain Admins - In the Domain Admins Properties, click the Members tab (the domain
name
will be different from yours)
![Domain Admins Properties]()
- Click Add...
- In the Enter the Object Names to Select text box of the Select
Users,
Contacts, or Computers dialog box, type pkatts
![Select Users, Contacts, or Computers]()
- Click Check Names (in the result, the domain name will be
different from
yours)
![Select Users, Contacts, or Computers]()
- Click OK
- Click OK