In this article we will walk through and understand each function of the Object class.
System.Object is known as the mother class of all the managed classes. All the classes are inherited from System.Object. It is base type for all the managed classes. So it defines the base behavior of all the managed classes.
System.Object class contains the following functions.

Let us examine each function one by one.
For all the following explanations we will use Student class. Student class is as below.
class Student
{
public string RollNumber { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
Object.GetHashCode method
- This returns an integer.
- On overriding it returns unique identifier for instance
- Hash code for an instance can be calculated using simple algorithm to complex algorithm.
- We should be using a constant and Read only data to calculate the hash code. Because if data changes then hash value will also get changed.
In Employee class let us override the GetHashCode() method. We will be returning 100 times of roll number as hash value for the instance. Feel free to put any complex algorithm in the overridden method to calculate a hash value for the instance.
using System;
namespace ConsoleApplication8
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student { RollNumber = "1" };
int hash1 = student.GetHashCode();
Console.WriteLine(hash1);
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
}
class Student
{
public string RollNumber { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public override int GetHashCode()
{
//return base.GetHashCode();
return Convert.ToInt32(RollNumber)*100;
}
}
}

Object.GetType method
- This returns a Type object.
- This is mainly used for reflection.
- Type class is an abstract class and inherits MemberInfo class and implements _Type , IReflect interface
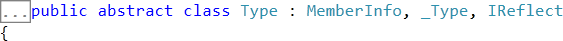
- This class contains many vital methods like Name, ReturnType etc.
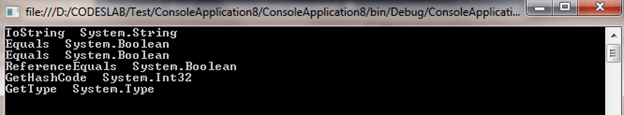
In the example below, we will print the type information of all the functions in the System.Object class.
using System;
using System.Reflection;
namespace ConsoleApplication8
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Object obj = new Object();
Type type = obj.GetType();
foreach(MethodInfo mn in type.GetMethods())
{
Console.WriteLine(mn.Name + " " + mn.ReturnType);
}
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
}
Object.ToString method
- This method is one of the widely used methods.
- This returns string representation of the instance.
- It returns fully qualified name of the type.
- For primitive type it is overridden and returns string values.
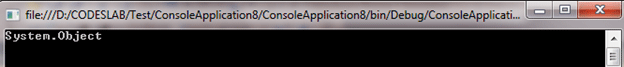
In the example below, we will convert an instance of an Object class to a string.
using System;
using System.Reflection;
namespace ConsoleApplication8
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Object obj = new Object();
Console.WriteLine(obj.ToString());
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
}
Object.Equals method
- Two References are equal only if they are pointing to the same object.
- Two references are not equal if they are pointing to different objects.
- For value types Equals is overridden and returns the comparison of values
- Equals method can be overriden.
In the example below, we are overriding the Equals() method in Student class. Ee are overriding Equals() method and not overriding GetHashCode(). We should override both the methods to avoid unexpected result.
Two objects are equal if they have the same hash value.
using System;
using System.Reflection;
namespace ConsoleApplication8
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student s1 = new Student { RollNumber = "1", Name = "Scott" };
Student s2 = new Student { RollNumber = "1", Name = "Scott" };
bool result = s1.Equals(s2);
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
}
class Student
{
public string RollNumber { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
//return base.Equals(obj);
if (obj == null)
return false;
return this.GetHashCode() == -obj.GetHashCode();
}
}
}

Object.ReferenceEquals method
- If two objects are same it returns true.
- It is not virtual and cannot be overridden.
- It compares identity of two objects.
using System;
using System.Reflection;
namespace ConsoleApplication8
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student s1 = new Student { RollNumber = "1", Name = "Scott" };
Student s2 = new Student { RollNumber = "1", Name = "Scott" };
bool result = Student.ReferenceEquals(s1, s2);
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
}
class Student
{
public string RollNumber { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
