Meta elements provide information about a given Web page, most often to help search engines categorize them correctly. They are inserted into the HTML document, but are often not directly visible to a user visiting the site or, Metadata is information about data. The <meta> tag provides metadata about the HTML document. Metadata will not be displayed on the page, but will be machine parsable. The HTML <meta> tag is used for declaring metadata for the HTML document. Metadata can include document description, keywords, author etc. It can also be used to refresh the page or set cookies. The meta tag is placed between the opening/closing <head> </head> tags.
Attributes
HTML tags can contain one or more attributes. Attributes are added to a tag to provide the browser with more information about how the tag should appear or behave. Attributes consist of a name and a value separated by an equals (=) sign, with the value surrounded by double quotes.
There are 3 kinds of attributes that you can add to your HTML tags: Element-specific, global, and event handler content attributes.
Element-Specific Attributes
The following table shows the attributes that are specific to this tag/element.
| Attributes Introduced by HTML5 |
| Attributes |
Value |
Description |
| Name |
author, description
keywords, generator
revised, others |
Provides a name for the information in the content attribute. |
| content |
text |
Specifies the content of the meta information |
| http-equiv |
content-type, content-style-type
expires
set-cookie
others |
Provides an HTTP header for the information in the content attribute. |
Global Attributes
The following attributes are standard across all HTML 5 tags.
|
HTML5 Global Attributes |
| accesskey |
draggable |
style |
| class |
hidden |
tabindex |
| dir |
spellcheck |
|
| contenteditable |
id |
title |
| contextmenu |
lang |
|
Event Handler Content Attributes
Here are the standard HTML 5 event handler content attributes.
| onabort |
onerror* |
onmousewheel |
| onblur* |
onfocus* |
onpause |
| oncanplay |
onformchange |
onplay |
| oncanplaythrough |
onforminput |
onplaying |
| onchange |
oninput |
onprogress |
| onclick |
oninvalid |
onratechange |
| oncontextmenu |
onkeydown |
onreadystatechange |
| ondblclick |
onkeypress |
onscroll |
| ondrag |
onkeyup |
onseeked |
| ondragend |
onload* |
onseeking |
| ondragenter |
onloadeddata |
onselect |
| ondragleave |
onloadedmetadata |
onshow |
| ondragover |
onloadstart |
onstalled |
| ondragstart |
onmousedown |
onsubmit |
| ondrop |
onmousemove |
onsuspend |
| ondurationchange |
onmouseout |
ontimeupdate |
| onemptied |
onmouseover |
onvolumechange |
| onended |
onmouseup |
onwaiting |
For example
Content Attribute
The required content attribute specifies the content of the meta information. The value of the content attribute depends on the value of the name or http-equiv attribute.
<html>
<head>
<meta name="description" content="About article" />
<meta name="keywords" content="C#,asp.net,vb.net,sqlserver" />
<meta name="author" content="Rohatash" />
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8" />
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Name Attribute
The name attribute provides a name for the information in the content attribute. The value of the name attribute depends on the value of the content attribute. If the http-equiv attribute is set, the name attribute should not be set.
<html>
<head>
<meta name="description" content="About article" />
<meta name="keywords" content="C#,asp.net,vb.net,sqlserver" />
<meta name="author" content="Rohatash" />
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
http-equiv attribute
This attributes Provides an HTTP header for the information in the content attribute. The following example demonstrates how to use the <meta> tag to redirect to another web page.
<html>
<head>
<title>Meta Refresh Example</title>
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="4;url=http://www.vbdotnetheaven.com/" />
</head>
<body style="background-color:#ff9900;">
<p>Watch me redirect to another page in 4 seconds...</p>
</body>
</html>
Internet Explorer
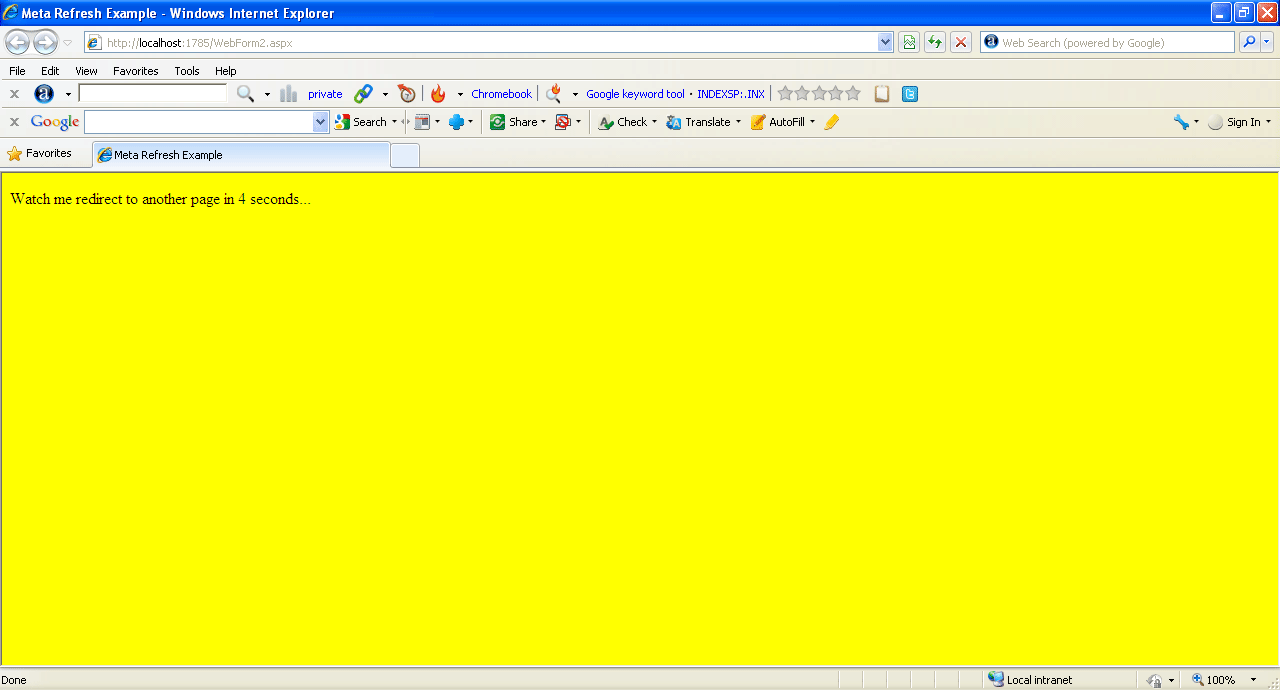
Figure1
After 4 seconds this page will be redirected to vbdotnetheaven.com.
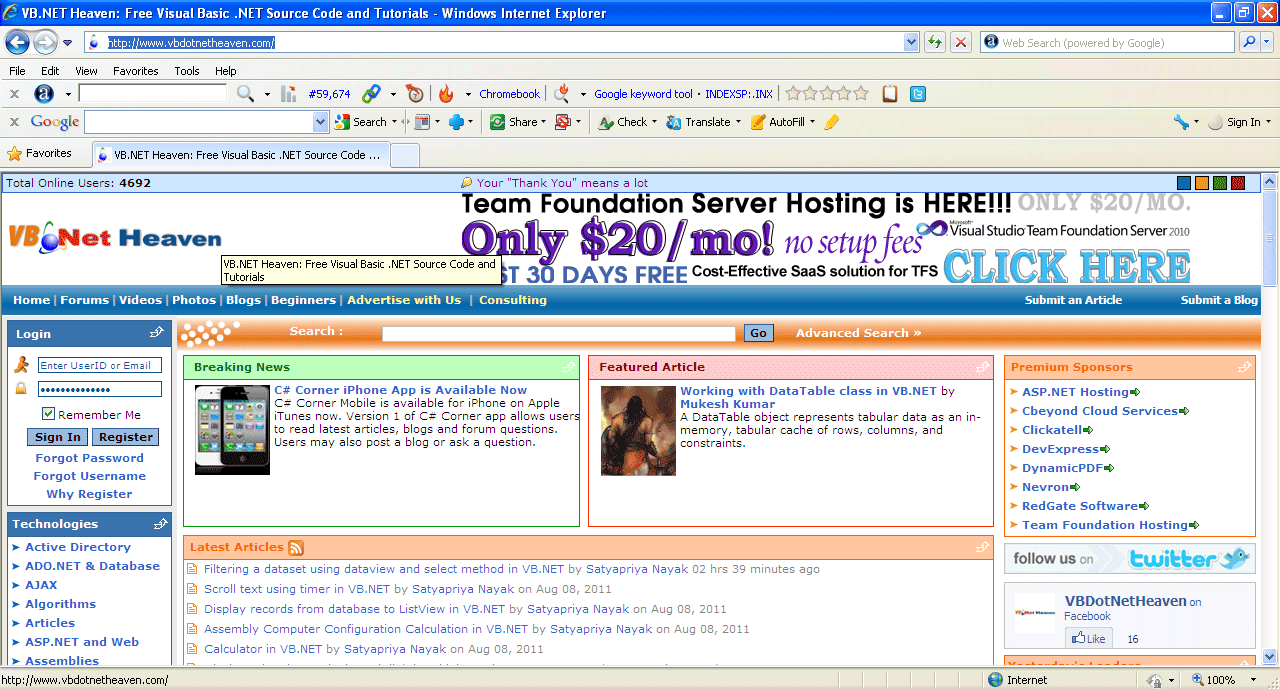
Figure2
Fire Fox
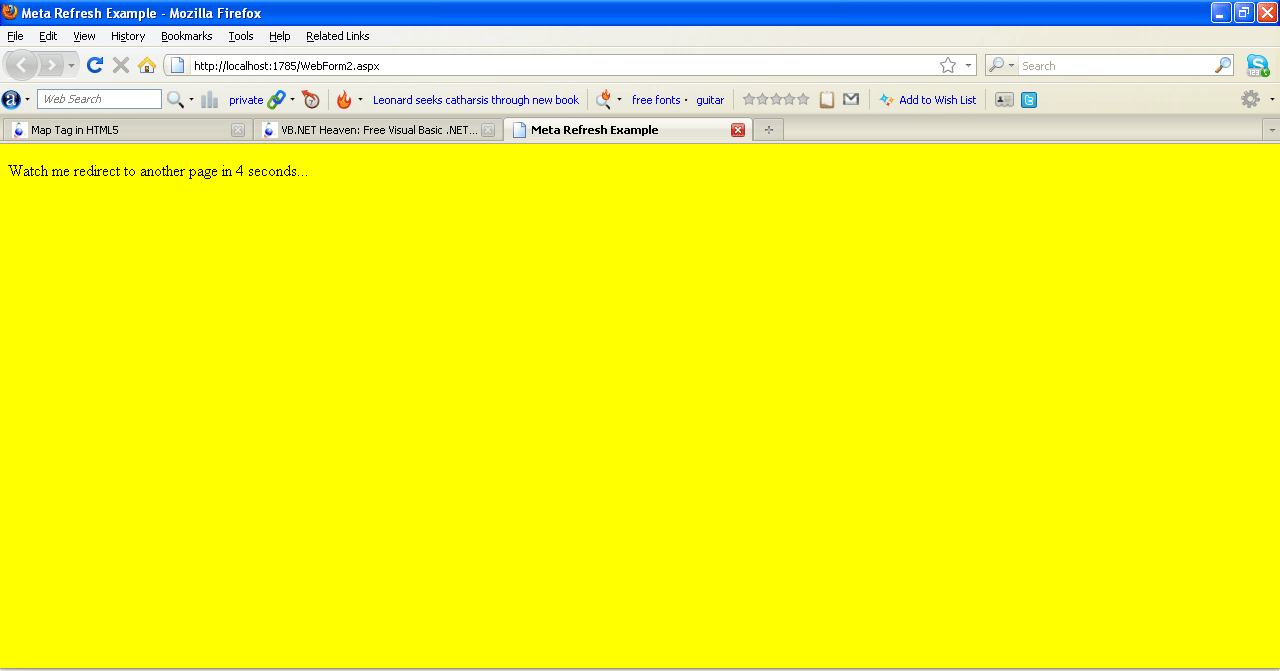
Figure3