If you have not read my article Resolving Concurrency conflicts in LINQ then I strongly recommend that you read it first. This article is a simple added extension of the previous article.
After reading resolving concurrency conflict in LINQ you are pretty much aware of mechanisms for concurrency conflict resolution. Now assume a requirement that you need to print or fetch:
- Current value of an object
- Original value of an object in the context
- Current data base value.
This is very much possible by
- Enumerating over MemberConflicts of ChangeConflict object.
- Fetching MemberChangeConflict in object of MemberConflict
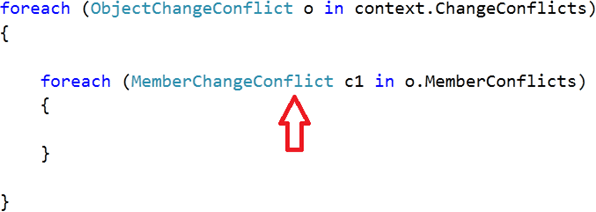
In child a foreach loop you can fetch values such as:

The Catch statement however should be modified as shown below to fetch and print multiple values.
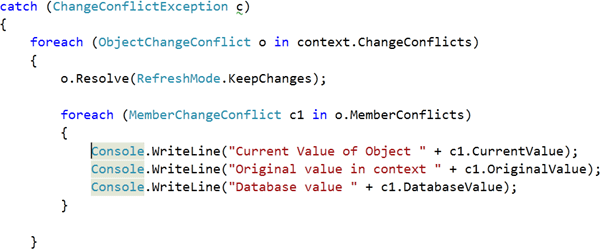
For reference you can find the full source code below:
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Data.Linq;
namespace Concurrency
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
DataClasses1DataContext context = new DataClasses1DataContext();
#region without handling Conflict
//Person personToUpdate = (from r in context.Persons
// where r.PersonID == 1
// select r).FirstOrDefault();
//personToUpdate.FirstName = "John Papa";
//context.SubmitChanges();
#endregion
#region hanlding conflict
try
{
Person personToUpdateConflict = (from r in context.Persons
where r.PersonID == 1
select r).FirstOrDefault();
personToUpdateConflict.FirstName = "John";
context.SubmitChanges(ConflictMode.FailOnFirstConflict);
}
catch (ChangeConflictException c)
{
foreach (ObjectChangeConflict o in context.ChangeConflicts)
{
o.Resolve(RefreshMode.KeepChanges);
foreach (MemberChangeConflict c1 in o.MemberConflicts)
{
var currentValue = c1.CurrentValue;
var originalValue = c1.OriginalValue;
var dataBaseValue = c1.DatabaseValue;
Console.WriteLine("Current Value of Object " + c1.CurrentValue);
Console.WriteLine("Original value in context " + c1.OriginalValue);
Console.WriteLine("Database value " + c1.DatabaseValue);
}
}
context.SubmitChanges();
}
#endregion
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
}
}
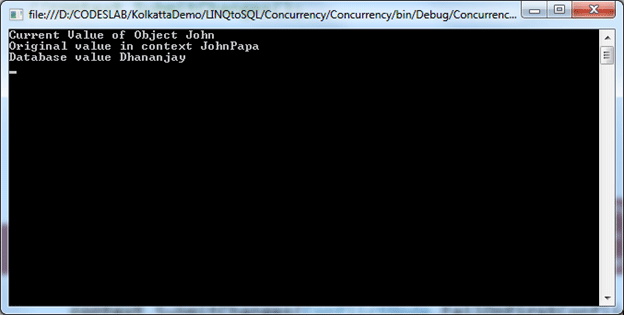
Upon execution of the application, you should get output as shown below.
I hope this article was useful. Thanks for reading.