Introduction
This post gives you the basic overview on ASP.NET Models, Views and Controllers. It explains how all parts in MVC Application work together and discuss how the Architecture of an ASP.NET MVC application differs from an ASP.NET Web Forms application.
The Sample ASP.NET MVC Application
- Launch Visual Studio 2008, Select the menu option File, New Project then New Project Dialogue box appear as shown below
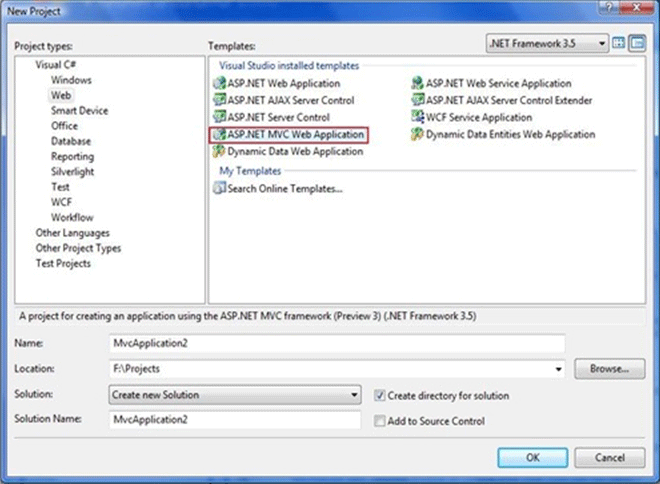
Select the ASP.NET MVC Web Application Template from the dialogue box and click Ok.
- When you create a ASP.NET MVC Application, Create Unit Test Dialogue box appears as shown below.
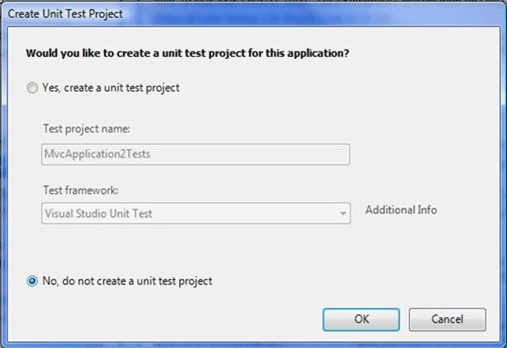
Select the No, do not create a unit test project and click Ok.
- After ASP.NET MVC Application is created. You will see several folders in Solution Explorer. You will find three folders named Models, Views and Controllers.
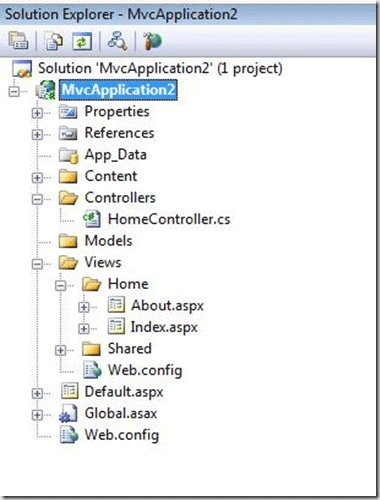
If you expand the Controllers Folder, you will see a file named HomeController.cs and if you expand the Views folder you will see About.aspx and Index.aspx under Home Sub Folder.
- Now you run the application you will see the following output
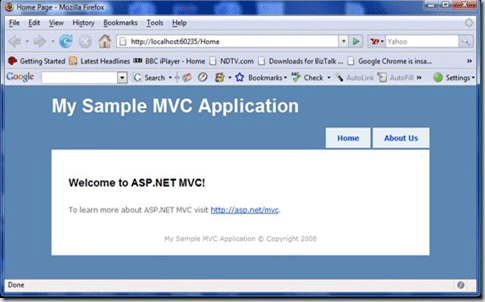
Notice the URL in the Address bar, When you click the Home menu link, The URL in the browser changes to /Home and when you click the About menu link, the URL changes to /About.
If you return to Visual Studio project you do not find the Home or About page.
A URL Does not Equal to a page in the application
- When you build a ASP.NET Web Application, there is a correspondence between a URL and Page. If you request a page test.aspx from the server then page must be on the disk other wise 404 - page not found error will come.
- When you build a ASP.NET MVC Application, there is no correspondence between URL and page that you found on the disk. Here a URL corresponds to a controller action instead of a page on the disk.
- In ASP.NET Web Application, Requests are mapped to pages. In ASP.NET MVC Application ,request are mapped to controller actions.
- ASP.NET Web Application is content-centric and MVC Application is logic centric.
URL Routing
- Here Browser Request is mapped to controller action through a feature called URL Routing. URL Routing route the incoming requests to controller actions.
- URL Routing uses Route Table that will be created when application first starts.
- Route table is setup in the Global.asax file.
The Default Global.asax file looks like
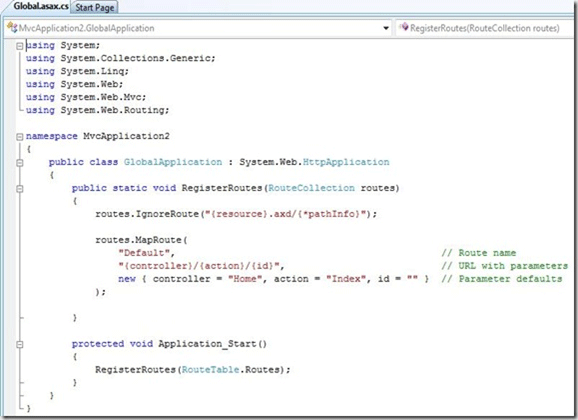
When ASP.NET Application first starts, the Application_Start() method is called. This method calls the RegisterRoutes() method which creates the default route table.
- Route table breaks the incoming request into 3 parts
- First part is mapped to a controller name, the second part is mapped to an action name and final part is a parameter that passed to the action.
Example: /Student/Details/3
This URL is parsed into three parts like this:
Controller = StudentController
Action = Details
Id = 3
If you run the sample ASP.NET MVC Application with out supplying a URL, the URL is parsed like this
Controller = HomeController
Action = Index
Id = ""
Controllers
A Controller is responsible for sending the response back to a user who makes the request. Controller is just a C# class file. The Sample MVC Application contains the controller named HomeController.cs located in the Controllers folder.
The Controller in the ASP.NET MVC Application looks like
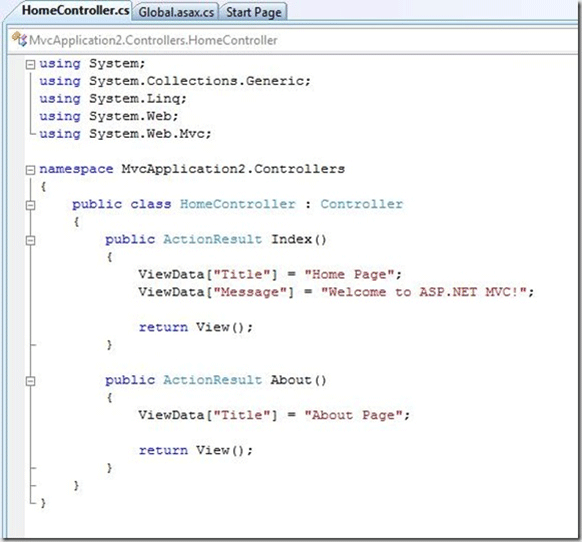
Note: The two methods in the controller Index() and About() corresponds to two actions Home and About clicks.
Views
- A view in the ASP.NET MVC Application contains the HTML elements and content that is sent to the browser.
- The two actions in the controller return a view.
- A View is equivalent to a page in ASP.NET MVC Application.
The HomeController.Index() action returns a view located in the following path
\Views\Home\Index.aspx
If you want to return a view for a controller action, you need to create a sub folder in the Views folder same name as controller and create a .aspx file with same name as the action.
Models
A Model in ASP.NET MVC Application contains logic that is not in the view or a controller. The Model should contain your business logic and Data access logic.
Conclusion
We had a overview on ASP.NET MVC application and URL Routing. We learnt the functionality of Model, Controller and View in the ASP.NET MVC Application.