Introduction
This post explains how to represent business objects with the ObjectDatasource control. It allows you to bind DataBound controls such as GridView, DetailsView and FormView. It also enables you to separate your business logic and data access logic from presentation layer.
The following types can be the data source for the ObjectDataSource Control
- Collections
- ADO.NET Objects
- LINQ to SQL
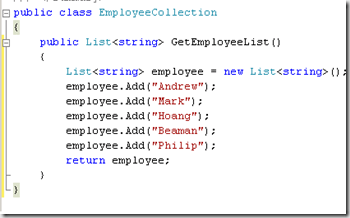
Collections

You can use the SelectMethod Property for selecting data from a method and TypeName is the type of the object that you are using as source for ObjectDataSource Control.
The sample Type is as follows
Now you can use DataBound controls to bound to the ObjectDataSource control through DataSourceID property.
LINQ to SQL Query
The preferred method of data access is LINQ to SQL. The type can be looks like
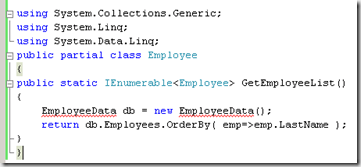
Assuming that you have already created the datacontext for LINQ to SQL.
Using Parameters with the ObjectDataSource Control
We can use Select,Insert,Update,Delete and Filter parameters when calling the method with the ObjectDataSource Control.
For example we can write a Update method in the type as follows
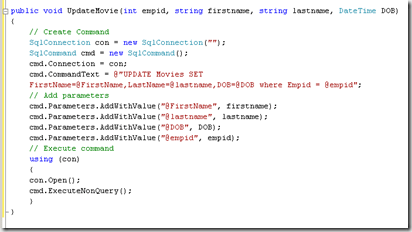
The UpdateMethod property of ObjectDataSource control can point to the above method. When you bound this datasource to GridView control it automatically adds the update parameters to the ObjectDataSource control's UpdateParameter's collection. It uses reflection to match the parameters against method parameters.
Paging, Sorting, and Filtering Data with the ObjectDataSource Control
The ObjectDataSource Control provides two options for paging and Sorting.
- UserInterface Paging
- DataSource Paging
In order to use UserInterface paging you need to bind the GridView control to DataSet, DataView or DataTable. The Drawback of using this option is all the records are loaded into server memory.
In DataSource Paging you can write custom logic or storedprocedure to perform the paging.
Adding and Modifying Parameters
You can use Selecting, Inserting, Updating and Deleting events of ObjectDataSource Control to modify the parameters that are passed to the methods.
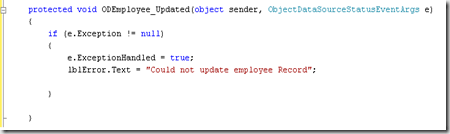
Handling Errors
You can use Selected,Inserted,Updated or Deleted events in order to handle any errors that results from the methods.
Example: