We have already discussed in my previous article that the LinearLayout arranges views in a single column or single row. It displays child View elements in a linear direction, either vertically or horizontally. Like a box it contains controls inside; controls are drawn one after each other either horizontally or vertically according to the Orientation of the layout.
When dealing with Linear layout there are five properties that we can deal with:
- Orientation
- Fill model
- Weight
- Gravity
- padding
As you have already learned the first three categories, in this article I am going to explain the remaining two categories Gravity and Padding.
- Gravity: By default widgets are positioned in the top-left of the screen but if you want you can specify the "gravity" for each component that's in the LinearLayout. This determines whether the component is left or right aligned, and top or bottom aligned, or a combination of these.
Basically we use six types of gravity properties with LinearLayout:
--left
--center
--center_vertical
--center_horizontal
--right
--bottom
I know based on the above documentation it was not very clear how the above layout parameters work. So, I read and find out more details and finally understood how to use gravity with LinearLayout. I will explain these properties with examples:
left gravity
<TextView
android:layout_gravity="left"
android:background= "#aa0000"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:text="TextView with Left Gravity"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"/>
Output:

center gravity
<TextView
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background= "#00aa00"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:text="TextView with center Gravity"
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"/>
Output:
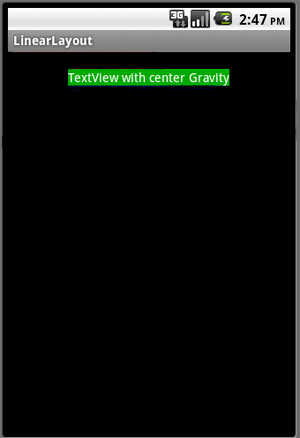
center_vertical gravity
<TextView
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:background= "#0000aa"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:text="TextView with center vertical Gravity"
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content" />
Output:
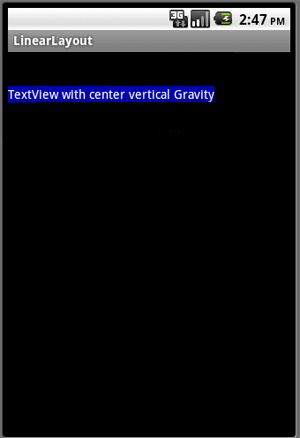
center_horozontal gravity
<TextView
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background= "#00FFFF"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:text="TextView with center horizontal Gravity"
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content" />
Output:

right gravity
<TextView
android:layout_gravity="right"
android:background= "#FF00FF"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:text="TextView with right Gravity"
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content" />
Output:

bottom
<TextView
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:background= "#0999ff"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:text="TextView with bottom Gravity"
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content" />
Output:

Here is the complete application to understand all properties of gravity in a single application:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_gravity="left"
android:background= "#aa0000"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:text="TextView with Left Gravity"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background= "#00aa00"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:text="TextView with center Gravity"
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:background= "#0000aa"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:text="TextView with center vertical Gravity"
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background= "#00FFFF"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:text="TextView with center horizontal Gravity"
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:layout_gravity="right"
android:background= "#FF00FF"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:text="TextView with right Gravity"
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:background= "#0999ff"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:text="TextView with bottom Gravity"
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout >
Output:
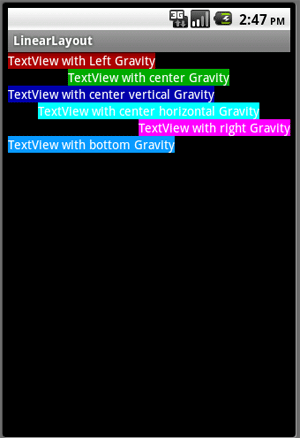
-
Padding: The "android:padding" property sets the padding between widgets. If you specify the padding property to the container then the container with all of its widgets would be shifted by the value, if you specify it to a single widget then the contents of that widget would be shifted by the specified value.
I set the layout_height property to "wrap_content" which means the height of the TextView should be increased according to the size of text, but because I use the padding property the height of the TextView is increased according to the size of the text as well as the value of "android:paddingTop".
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingTop="20px"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView
android:text= "First Layout"
android:background= "#aa0000"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:layout_width= "fill_parent"
android:paddingTop="20px"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:text= "Second Layout"
android:background= "#00aa00"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:layout_width= "fill_parent"
android:paddingTop="20px"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:text= "Thired Layout"
android:background= "#0000aa"
android:textColor="#ffffffff"
android:layout_width= "fill_parent"
android:paddingTop="20px"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
Output:
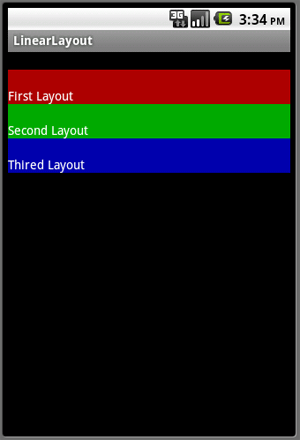
I hope you enjoy learning how to work with LinearLayout in Android using Visual Studio 2010.