Introduction
What is Biztalk Server
- Biztalk is a messaging based integration tool.
- BizTalk Server is designed specifically to integrate disparate systems.
- Microsoft BizTalk Server 2006 provides a development and run-time environment for business process management (BPM) and automation.
- Biztalk is a collection of components that all seek to accomplish integration.
- Microsoft BizTalk Server is used to connect systems both inside and across organizations. This includes exchanging data and orchestrating business processes
- BizTalk Server helps organizations create automated business processes :
- Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) means connect applications within a single organization.
- Business-to-Business Integration (B2B) means connect applications across different organizations.
- BizTalk Server can coordinate with other servers.
- Exchange Server
- Content Mgmt Server
- Integration host server(SAP,ERP)
- Sharepoint Server
- BizTalk Server can coordinate with other Dotnet components
- WCF
- WF
- SSIS
- SSAS
- BizTalk Server can coordinate with MS-Office specially with Infopath.
BizTalk server Hosts and Host Instances
A BizTalk Host is a set of running engines—BizTalk Message Queuing (MSMQT), XLANG, and Tracking Data Decode Service (TDDS).These services communicate with the MessageBox database. A BizTalk Host is a logical set of zero or more BizTalk runtime processes in which we deploy items such as adapter handlers, receive locations (including pipelines), and orchestrations. A host instance is the place where the message processing, receiving, and transmitting occurs. We install a host instance on each BizTalk Server computer that has one or more hosts mapped to that server.
Hosts have the following characteristics:
- Hosts are the logical containers of BizTalk objects.
- Only one instance of a specific host can exist on one server.
- We can map one host to multiple servers.
Host instances have the following characteristics:
- Host instances running on the servers are the physical containers of BizTalk objects.
- Multiple host instances (of different hosts) can exist on a server.
BizTalk Components
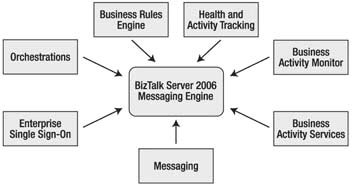
Figure 1. BizTalk Server 2006 Applications
Message Engine
The Messaging Engine is the core of BizTalk. This engine is responsible for ensuring that messages are received and routed to the proper location, transaction isolation and consistency occurs and errors are reported. The Messaging Engine uses several BizTalk databases to store message information and metadata as well as system-level parameters. The Messaging Engine uses Microsoft SQL Server as its data storage facility. The central database for messages within BizTalk is called the Messagebox. SQL Server is not required to be physically installed on the same machine as BizTalk Server.
Lifecycle of a Message
A message is received through a receive location defined in a given receive port. This message is processed by the receive location and then published to the MessageBox database. The MessageBox evaluates active subscriptions and routes the message to those orchestrations and send ports with matching subscriptions. If it is routed to the orchestration then orchestration processes the message and publish message through the MessageBox to a send port and then it is pushed out to its final destination.
MessageBox: Database on the Sqlserver.
Message-Delivery Patterns describe the particular way in which BizTalk consumes and produces the messages. "Publish-subscribe"Message-Delivery Patterns is used by Biztakserver.
Note: Details of the Message engine and lifecycle of the message will be covered in next series of articles.