CORBA-IIOP And DCOM In Oracle
CORBA/IIOP And DCOM
CORBA stands for Common Object Request Broker Architecture.
• CORBA is created by a union of over 600 companies.
• CORBA contains opens specification for ORB and IDL.
• CORBA supports cross-platform deployment.
• Allows object instances to exist and have persistent state.
The principle goal of CORBA is to encourage the use and integration of objects, regardless of the language used to construct the object and the operating system, where it resides.
• CORBA provides a specification of Services.
• CORBA is selected as ORB by Oracle Software.
• Supports true inheritance of the objects.
• Specifies that ORB can talk to ORB in CORBA 2.0.
Thus, we learnt, CORBA/IIOP and DCOM. COBRA stands for Common Object Request Broker Architecture. IIOP stands for Internet Inter Object Request Broker Protocol (IIORB Protocol). DCOM stands for Distributed Common Object Model.
CORBA/IIOP
CORBA is a product of a union called the Object Management Group (OMG). CORBA is established in 1989, which includes over 600 companies representing the entire spectrum of the computer industry with the notable exception of Microsoft.
The current version of CORBA is 2.0, released on July 1995 and is updated in July 1996.
• CORBA contains opens specification for ORB and IDL.
• CORBA supports cross-platform deployment.
• Allows object instances to exist and have persistent state.
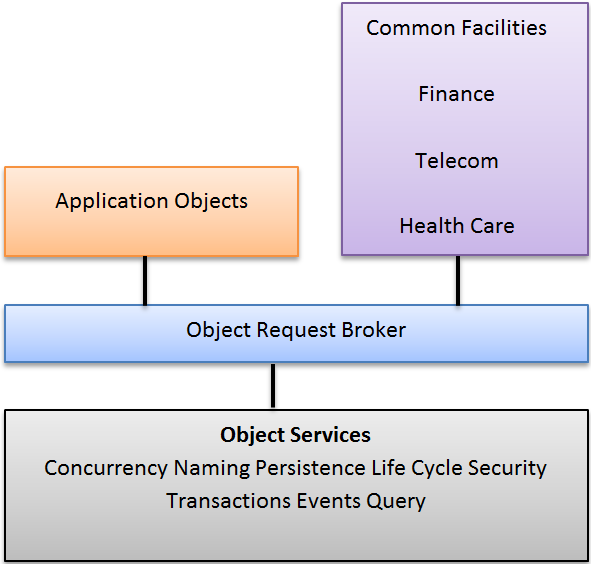
There are Applications like Finance, Telecom, Healthcare, which needs to access various data objects lying in a database. CORBA is a set of specification defining Client/Server middleware architecture.

Figure: CORBA Architecture
CORBA accomplishes this goal through the use of an ORB, which is a piece of software that handles the request for object Services. ORB is an object bus.
CORBA contains the specification for an Interface Definition Language (IDL), which provides a language independent description of the Service provided by an object.
CORBA architecture provides corporation with the following benefits-
• CORBA is selected as ORB by Oracle Software.
• Supports true inheritance of the objects.
• Specifies that ORB can talk to ORB in CORBA 2.0.
IIOP
IIOP stands for Internet Inter Object Request Broker Protocol (IIORB Protocol).
Internet Inter-ORB Protocol, a key protocol for building distributed object Applications, such as an Application for the internet and the World Wide Web (www).
IIOP uses the internet based on TCP/IP as a backbone for Object Request Broker to communicate with each other.
DCOM
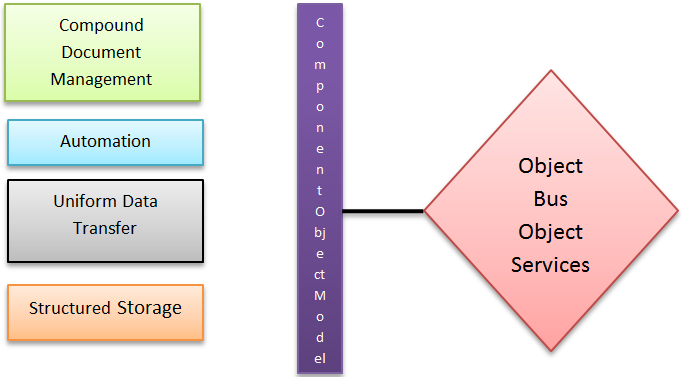
DCOM stands for Distributed Common Object Model. DCOM is developed by Microsoft. It contains different IDL (Interface Definition Language) syntax from CORBA. DCOM supports mainly Window platforms. DCOM allows distributed object instances to be created but not with the persistent state.

Figure: DCOM Architecture
Summary