How To Use Primary Key In Oracle
Primary key in oracle
In Oracle, a primary key is a single field or a combination of fields. Primary key in a relational database is unique record for all the all tables. None of the fields, which are part of the primary key can contain a null value. There can be only one primary key in a table.
A primary key cannot contain more than 32 columns.
A primary key can be defined in either a create table statement and alter table statement.
Create table statement using Primary key
You can create a primary key in create table statement.
Syntax
- Create table table_name
- (
- Column 1 datatype(),
- Column 2 datatype(),
- . .
- . .
- . .
- Column n datatype()
- Constraint constraint_name primary key(column 1, column 2…..column n)
- );
- Commit;
Example
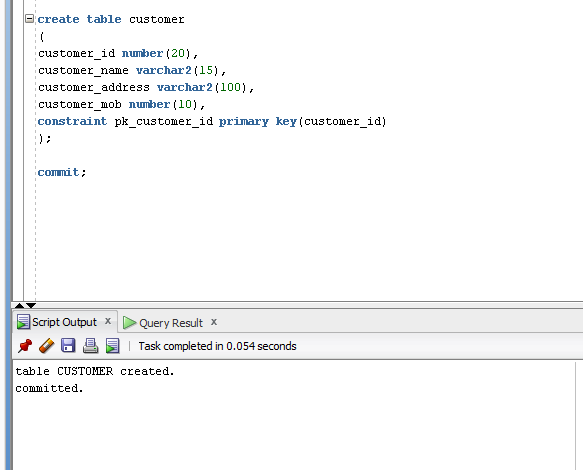
Look at an example, we can create a primary key in create table statement.
- Create table customer
- (
- Customer_id number(20),
- Customer_name varchar2(15),
- Customer_address varchar2(100),
- Customer_mob number(10),
- Constraint pk_customer_id primary key (customer_id)
- );
- Commit;
Drop Primary key
You can drop a primary key, using an alter table statement.
Syntax
Drop a primary key, using an alter table statement.
- alter table table_name
- Drop constraint constraint_name;
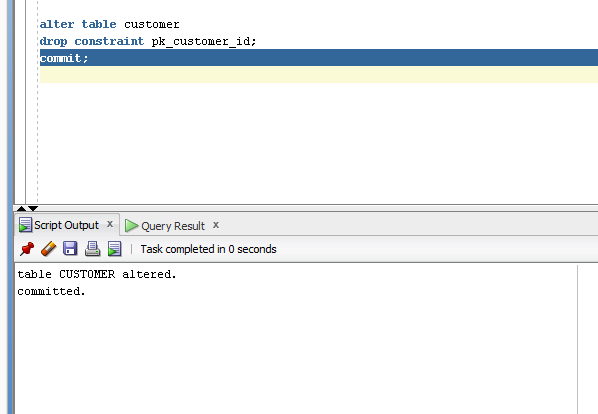
Example
- Alter table customer
- Drop constraint pk_customer_id;
- Commit;
Disable Primary Key
You can disable the primary key, using an alter table statement.
Syntax
Disable a primary key, using an alter table statement.
- Alter table table_name
- Disable constraint constraint_name;
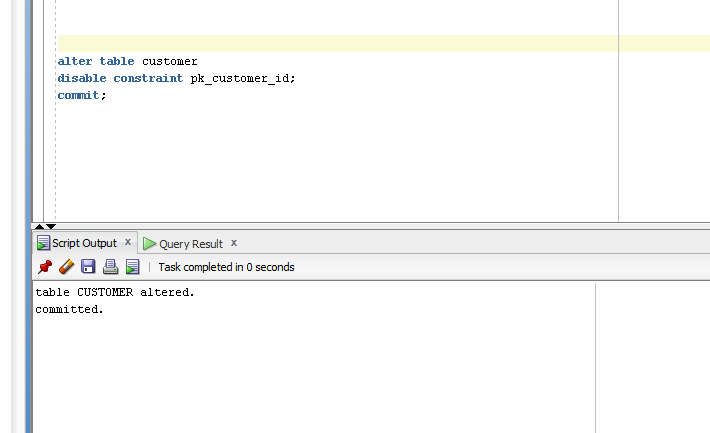
Example
- Alter table customer
- Disable constraint pk_customer_id;
- Commit;
Enable a primary key
You can enable a primary key, using an alter table statement.
Syntax
- Alter table table_name
- Enable constraint constraint_name;
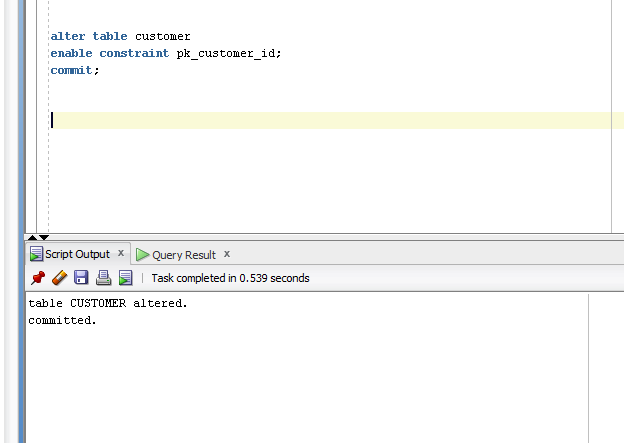
Example
- Alter table customer
- Enable constraint pk_customer_id;
- Commit;
Summary