How To Create, Update and Drop Views In Oracle
VIEW
Description
A view is the representation of a SQL statement, which is stored in the memory, so that it can be reused easily.
A view is also called a virtual table, stored query and the Window.
A view is also called a virtual table, stored query and the Window.
- View is used to restrict an access to the data of a table.
- View is used to simplify the query.
- View is used to increase the data independence.
- It is not possible to modify the structure of a table, using view.
- All views are stored in view.
Types of view
- Simple view
- Complex view
- Force view
- Vertical view
- Horizontal view
- Functional view
- Partition view
- Materialized view
- Inline view
Simple view is used to define a view on a single table.
Syntax
- Create view view_name
- AS
- Select * from Table_name;
Example
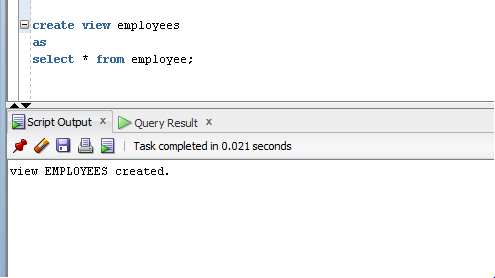
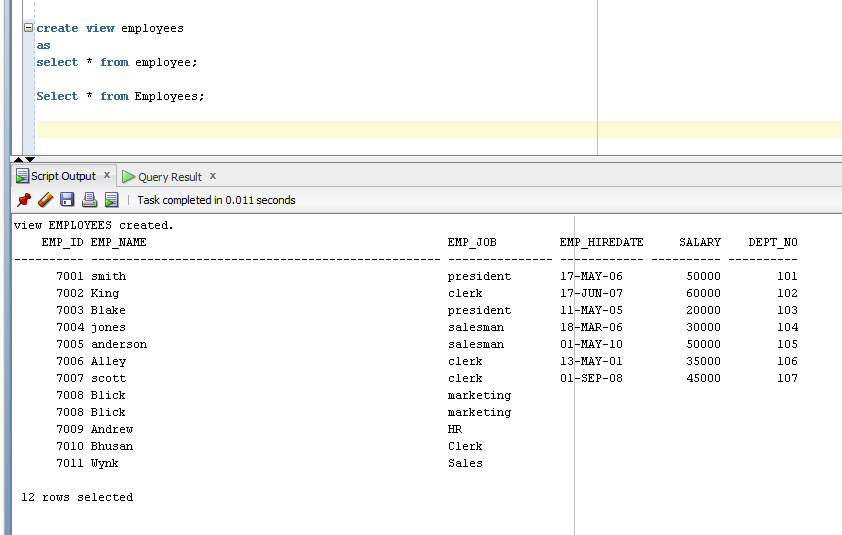
- Create View Employee
- AS
- Select * from Employee;
- Select * from Employees;
Complex View
Complex View is used to define a view on the multiple tables.
Syntax
- Create view view_name
- AS
- Select * from Emp, Dept
- Where Emp.Dept_no = Dept.Dept_no;
- Create view Employees
- AS
- Select * from Emp, Dept
- Where Emp.Dept_no = Dept.Dept_no;
Force View
Force View is used to define a view without a base table.
Syntax
- Create Force view view_name
- AS
- Select * from Non Existing table;
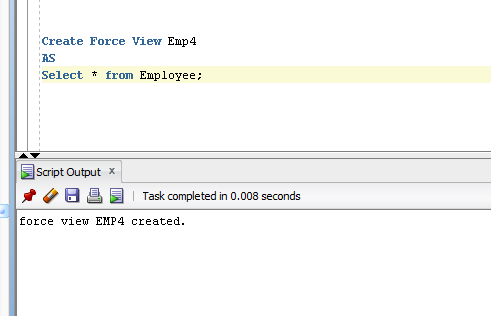
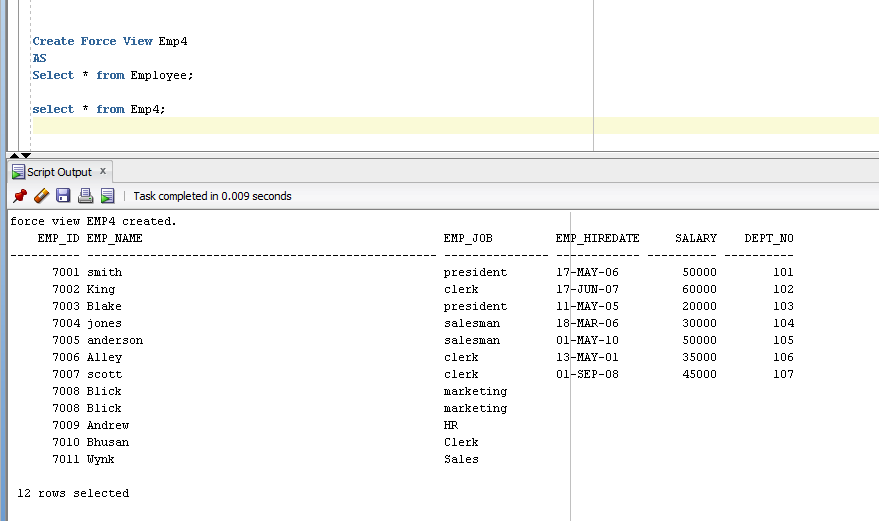
- Create Force View Emp4
- AS
- Select * from Employee;
Vertical View
Vertical view is used to define a view on the specific columns in a table.
Syntax
- Create view view_name
- AS
- Select Col1, col2..coln
- From Table_name;
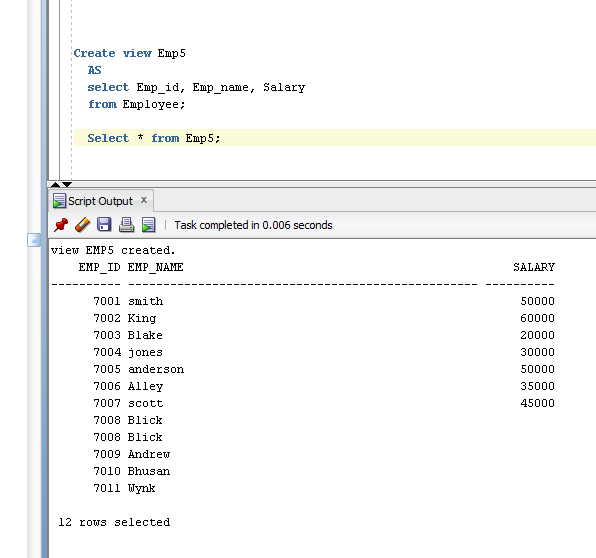
- Create view Emp5
- AS
- select Emp_id, Emp_name, Salary
- from Employee;
Horizontal View
Horizontal view is used to define a view on the specific column in the table.
Syntax
- Create view view_name
- AS
- select * from Table_name
- Where
- Dept_no=10;
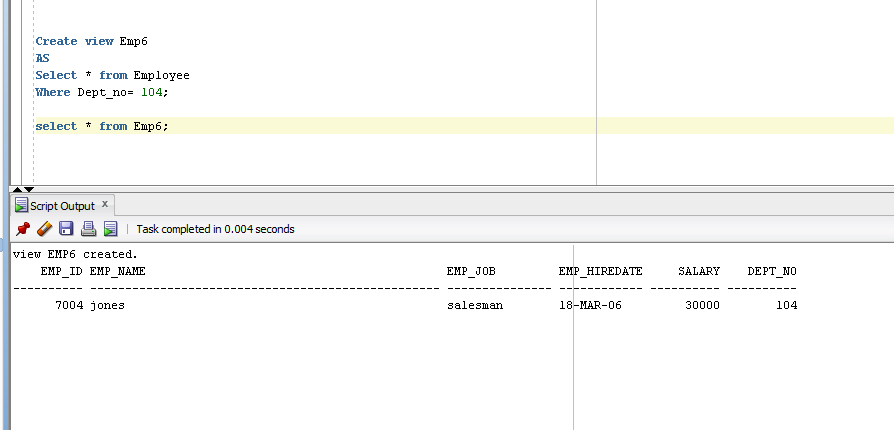
- Create view Emp6
- AS
- Select * from Employee
- Where Dept_no= 104;
Functional View
Functional view is used to define a view function on the table.
Syntax
- Create view view_name(col1, col2)
- AS
- Select Fun1, Fun2
- from Employee;
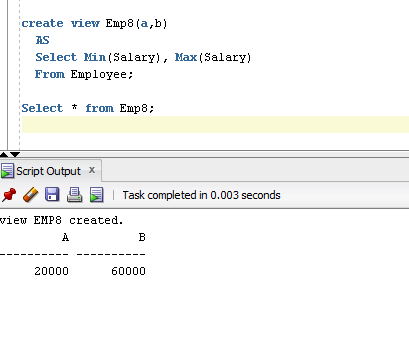
- create view Emp7(Emp_name, Salary)
- AS
- Select Min(Salary), Max(Salary)
- From Employee;
Partition View
Partition view is used to define a view on the compound query.
Syntax
- Create view view_name
- AS
- Query1 Union Query2;
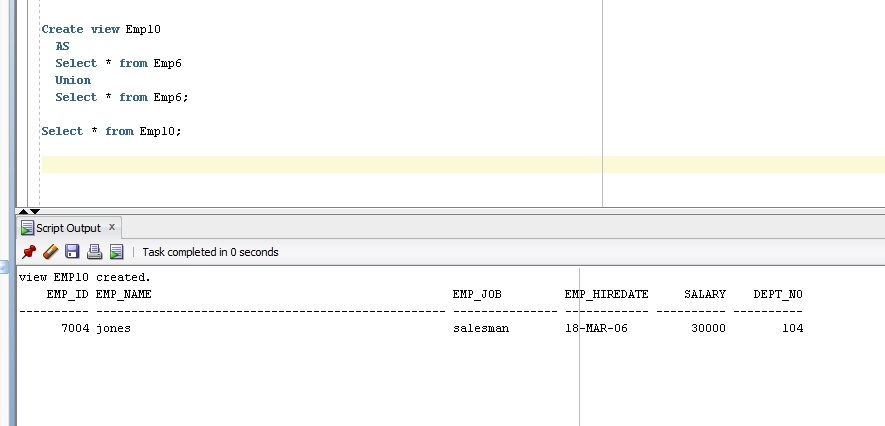
- Create view Emp10
- AS
- Select * from Emp6
- Union
- Select * from Emp6;
Materialized View
Materialized view is used to define a view, which is having the own structure.
it is used to store the historical data.
Syntax
- Create materialized view view_name
- AS
- Select * from Table_name;
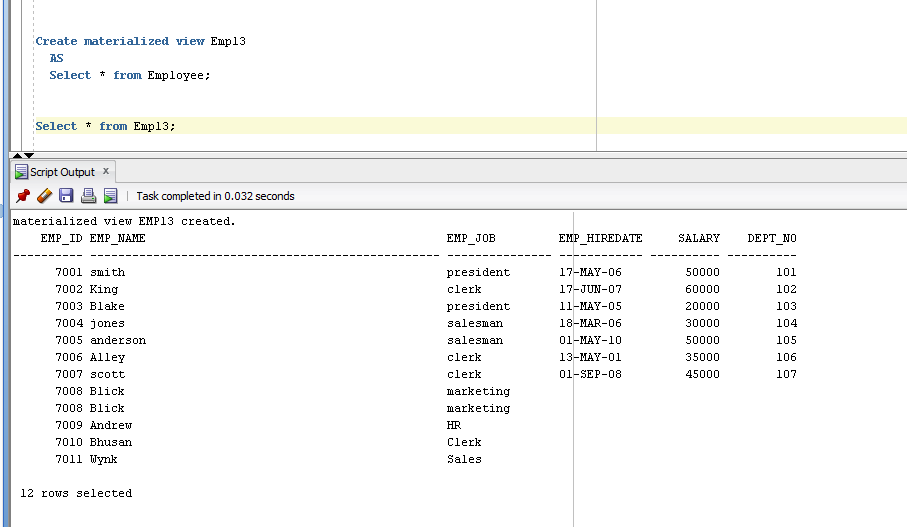
- Create materialized view Emp13
- AS
- Select * from Employee;
Inline view
Inline view works like a query.
Syntax
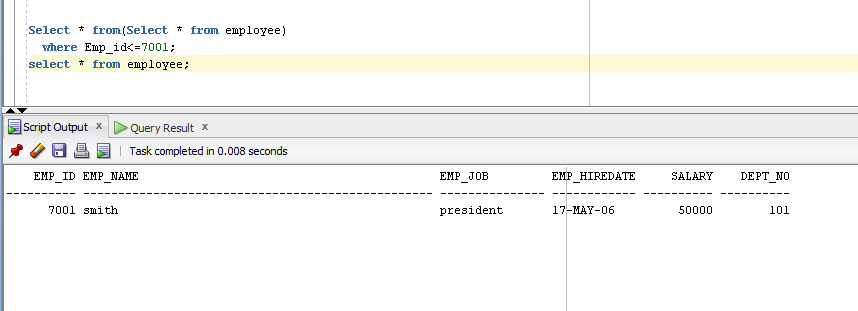
- Select * from(select * from Table_name);
- Select * from(Select * from employee)
- where Emp_id<=7001;
Update view
You can modify the view without dropping in Oracle.
Syntax
- Create or replace view view_name
- AS
- Select Columns
- From Table
- where conditions;
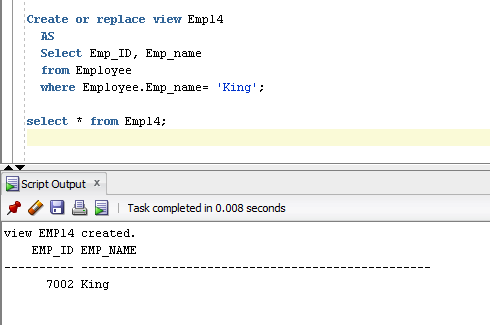
- Create or replace view Emp13
- AS
- Select Emp_ID, Emp_name
- from Employee
- where Employee.Emp_name= ‘King’;
Drop View
In this view, you want to drop a view, which is called drop view.
Syntax
- Drop view view_name;
Example
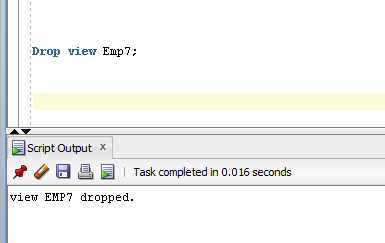
- Drop view Emp7;
Summary
Thus, we learnt, a view is the representation of a SQL statement, which is stored in the memory, so that it can be reused easily. A view is also called the virtual table, stored query and the Window. We learnt, how to use view with the examples.