HTML 5 Web SQL Database
- openDatabase
- transaction
- executeSql
var dbObj = OpenDatabase('[Database_Name]', '[Version_Number]', '[Text_Description]', '[size]', '[Creation_Callback]')
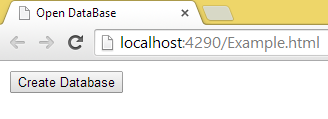
- First, create a button in your HTML 5 page as in the following:
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>Open Database</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <button id="btnCreateDB">Create Database</button>
- </body>
- </html>
-
Now create a JavaScript function to create the database as in the following:
- function CreateDB() {
- var Database_Name = 'MyDatabase';
- var Version = 1.0;
- var Text_Description = 'My First Web-SQL Example';
- var Database_Size = 2 * 1024 * 1024;
- var dbObj = openDatabase(Database_Name, Version, Text_Description, Database_Size, OnSuccessCreate());
- }
- function OnSuccessCreate() {
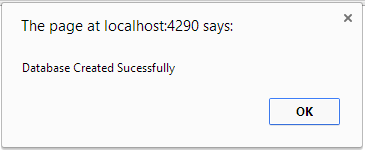
- alert('Database Created Sucessfully');
- }
-
Now bind this JavaScript function to the onclick event of the btnCreateDB button. The complete code is given below:
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>Open DataBase</title>
- <script>
- function CreateDB() {
- var Database_Name = 'MyDatabase';
- var Version = 1.0;
- var Text_Description = 'My First Web-SQL Example';
- var Database_Size = 2 * 1024 * 1024;
- var dbObj = openDatabase(Database_Name, Version, Text_Description, Database_Size, OnSuccessCreate());
- }
- function OnSuccessCreate() {
- alert('Database Created Sucessfully');
- }
- </script>
- </head>
- <body>
- <button id="btn1" onclick="CreateDB()">Create Database</button>
- </body>
- </html>
-
Now open this file, I am opening it in Google Chrome. By default the output will be:
-
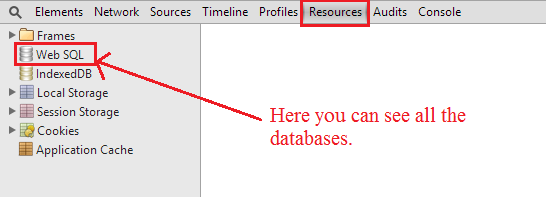
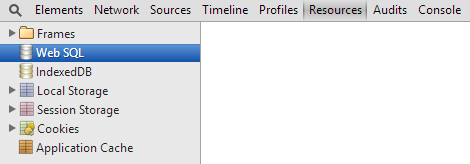
Now press the F12 function key and open the Google Chrome developer tool and open the Resource tab where you will get a Web SQL database.
-
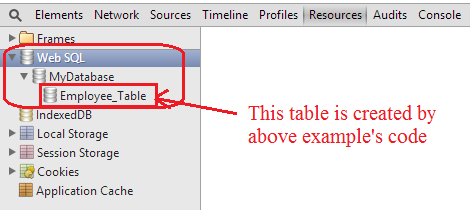
Now click on the Create Database button and you will get the following output.
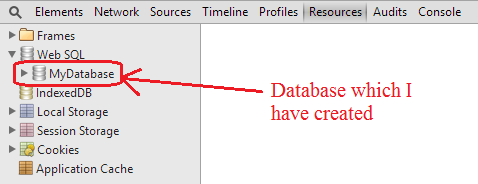
And inside the developer tool you will get the database.
- Database name: This argument provides the name of the database that is mandatory to be provided, otherwise you will get an exception.
- Version number: Version number is also required; some database may be in version 2.0 and may be in 1.0 so if you know the version number of the database then only you can open it.
- Text description: This argument describes the database and provides information about the database.
- Size of database: This argument decides the size of the database.
- Creation callback: This argument is optional, if you do not provide any value then the database will also be created but if you want to perform some action after creation of the database then you can use this, so if the database is created successfully then this work will be done.
- function CreateDB() {
- var Database_Name = 'MyDatabase';
- var Version = 1.0;
- var Text_Description = 'My First Web-SQL Example';
- var Database_Size = 2 * 1024 * 1024;
- var dbObj = openDatabase(Database_Name, Version, Text_Description, Database_Size);
- dbObj.transaction(function (tx) {
- //Code of the transaction
- //will goes here
- });
- }
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>Open DataBase</title>
- <script>
- function CreateDB() {
- var Database_Name = 'MyDatabase';
- var Version = 1.0;
- var Text_Description = 'My First Web-SQL Example';
- var Database_Size = 2 * 1024 * 1024;
- var dbObj = openDatabase(Database_Name, Version, Text_Description, Database_Size);
- dbObj.transaction(function (tx) {
- tx.executeSql('CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Employee_Table (id unique, Name, Location)');
- });
- }
- </script>
- </head>
- <body>
- <button id="Create_DB_n_Table" onclick="CreateDB()">Create Database & Table</button>
- </body>
- </html>
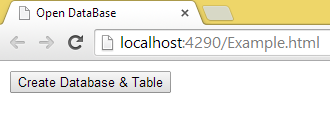
- When the page is loaded:
- If you then open the developer tool of Google Chrome then you will get the following output:
- After clicking on the button:
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>Open DataBase</title>
- <script>
- var Database_Name = 'MyDatabase';
- var Version = 1.0;
- var Text_Description = 'My First Web-SQL Example';
- var Database_Size = 2 * 1024 * 1024;
- var dbObj = openDatabase(Database_Name, Version, Text_Description, Database_Size);
- dbObj.transaction(function (tx) {
- tx.executeSql('CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Employee_Table (id unique, Name, Location)');
- });
- function Insert() {
- var id = document.getElementById("tbID").value;
- var name = document.getElementById("tbName").value;
- var location = document.getElementById("tbLocation").value;
- dbObj.transaction(function (tx) {
- tx.executeSql('insert into Employee_Table(id, Name, Location) values(' + id + ',"' + name + '","' + location + '")');
- });
- }
- </script>
- </head>
- <body>
- <form id="frm1">
- <table>
- <tr>
- <td>ID:</td>
- <td><input type="text" id="tbID" /></td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Name:</td>
- <td><input type="text" id="tbName" /></td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Location:</td>
- <td><input type="text" id="tbLocation" /></td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td><button id="btnInsert" onclick="Insert()">Insert</button></td>
- </tr>
- </table>
- </form>
- </body>
- </html>
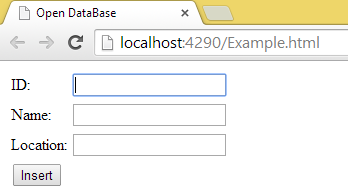
- When the page is loaded then:
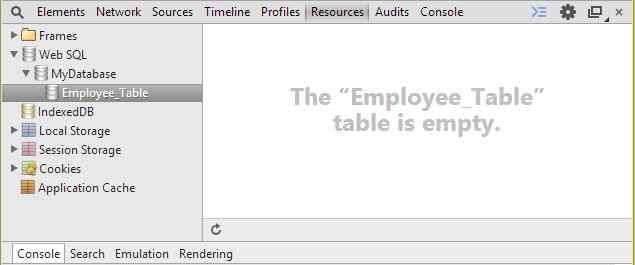
- If you look at the developers tool then you will get output like this:
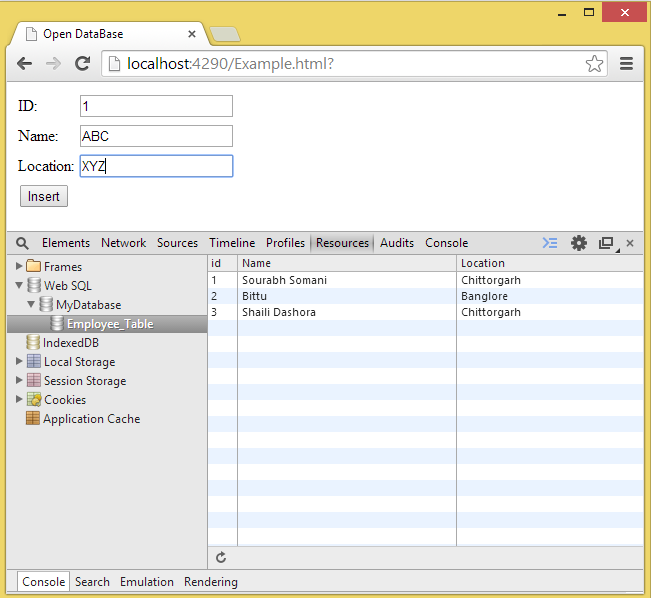
- When you fill in some data into the TextBoxes and submit it then:
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>Open DataBase</title>
- <script>
- var Database_Name = 'MyDatabase';
- var Version = 1.0;
- var Text_Description = 'My First Web-SQL Example';
- var Database_Size = 2 * 1024 * 1024;
- var dbObj = openDatabase(Database_Name, Version, Text_Description, Database_Size);
- dbObj.transaction(function (tx) {
- tx.executeSql('CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Employee_Table (id unique, Name, Location)');
- });
- function Insert() {
- var id = document.getElementById("tbID").value;
- var name = document.getElementById("tbName").value;
- var location = document.getElementById("tbLocation").value;
- dbObj.transaction(function (tx) {
- tx.executeSql('insert into Employee_Table(id, Name, Location) values(' + id + ',"' + name + '","' + location + '")');
- });
- }
- dbObj.transaction(function (tx) {
- tx.executeSql('SELECT * FROM Employee_Table', [], function (tx, results) {
- var len = results.rows.length, i;
- var str = '';
- for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- str += "<tr>";
- str += "<td>" + results.rows.item(i).id + "</td>";
- str += "<td>" + results.rows.item(i).Name + "</td>";
- str += "<td>" + results.rows.item(i).Location + "</td>";
- str += "</tr>";
- document.getElementById("tblGrid").innerHTML += str;
- str = '';
- }
- }, null);
- });
- </script>
- </head>
- <body>
- <p id="hh"></p>
- <form id="frm1">
- <table>
- <tr>
- <td>ID:</td>
- <td><input type="text" id="tbID" /></td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Name:</td>
- <td><input type="text" id="tbName" /></td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Location:</td>
- <td><input type="text" id="tbLocation" /></td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td><button id="btnInsert" onclick="Insert()">Insert</button></td>
- </tr>
- </table>
- </form>
- <table id="tblGrid" cellpadding="10px" cellspacing="0" border="1">
- <tr style="background-color:black;color:white;font-size:18px;">
- <td>
- ID
- </td>
- <td>
- Name
- </td>
- <td>
- Location
- </td>
- </tr>
- </table>
- </body>
- </html>
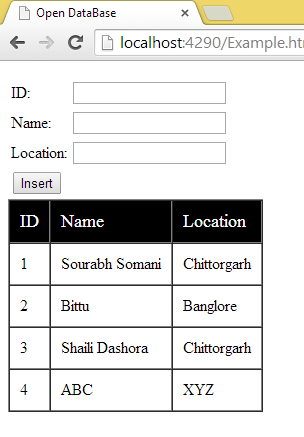
The following is the output of the code above:
Note that Web SQL Databases were on the W3C Recommendation track but specification work has stopped because all interested implementors use Sqlite and multiple independent implementations are necessary for a standard.