Python Tuple
Introduction
In this chapter, you will learn what Python tuple is and how is it useful?
Every programming language supports the basic data structure as a sequence and to store the data in sequence or store co-related data as a sequence.
Python supports six built-in sequences but most common are list and tuple.
Python also has a built in function for the manipulation and performing an operation on the tuple.
Python tuple
Tuple is a versatile data type of Python. The tuple can support any data type element in the same tuple.
Python tuple element is separated by comma(,).
Syntax of tuple-
tuple_name=(tuple_element)
Example-
tuple=(“c#corner”,1998)
Accessing value from tuple-
To access an individual value, the tuple must use square brackets with an index for slicing an individual value.
Example-
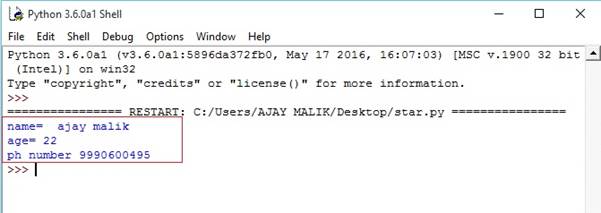
- tuple1 = ("ajay malik", 22, 9990600495)# tuple with the name number and ph number.
- print("name= ", tuple1[0])# prints the first element form tuple
- print("age=", tuple1[1])# prints the second element fot tuple
- print("ph number", tuple1[2])# prints third element from tuple
Output-
Updating tuple in python
We can’t update a tuple because tuple is immutable, which means tuple have a constant value.
Deleting tuple element
Deleting of an individual value from the tuple is impossible but we can delete whole tuple.
Example-
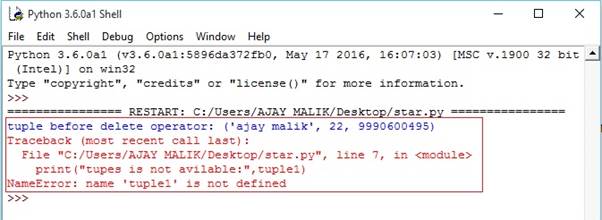
- tuple1 = ("ajay malik", 22, 9990600495)# tuple with the name number and ph number
- print("tuple before delete operator:", tuple1)
- del tuple1
- print("tupes is not avilable:", tuple1)
Output-
tuple operations
Python list is almost similar to string but list slightly different
Most common operations are listed below-
tuple1=(1,2,3) and tuple2(4,5,6)
| Operation | Expression | Result |
| Membership | 3 in tuple1 | True |
| Length | len(tuple1) | 3 |
| +(concatenation) | tuple1+tuple2 | (1,2,3,4,5,6) |
| Iteration | For item in tuple1: print(item) | 123 |
Indexing, slicing and matrixes
Indexing, slicing and matrixes works similar to the string.
Tuple1=(‘hello’,’Hello’,’HELLO’)
| Expression | Result | Description |
| tuple1[1] | Hello | Item at index 1 start from 0 |
| tuple1[-1] | Hello | Count from right |
| tuple1[1:] | [‘Hello’,’HELLO’] | Start from 1 to end |
Built-in list function are given below-
1) len(tuple1)
It counts the length of the list and returns the number of elements in the list.
Syntax-
len(tuple)
Return value- It returns a number or a length of the tuple.
Example-
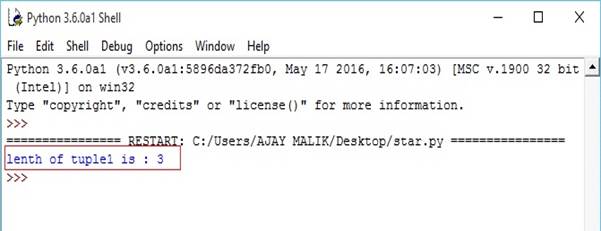
- tuple1=(1,2,3)
- tuple2=(4,5,6)
- n=len(tuple1)
- print("lenth of tuple1 is :",n)
Output-
2) max(tuple)
It finds the maximum value in the tuple and returns the maximum value.
Syntax-
max(tuple)
return value- maximum value from tuple
Example-
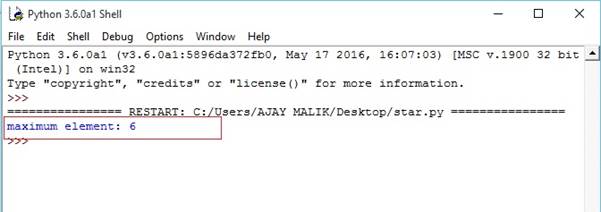
- tuple1=(1,2,3,4,5,6) #return maximum
- m=max(tuple1) #print max element
- print("maximum element:",m)
Output-
3) min(tuple)
It finds the minimum value element and returns the minimum value element.
Syntax-
min(tuple)
return value:- It returns the minimum value element.
Example-
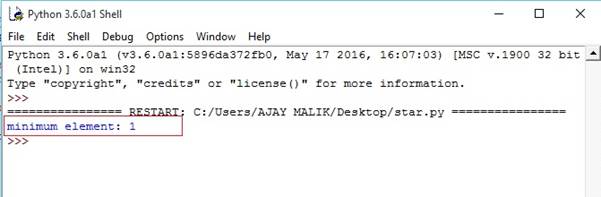
- tuple1=(1,2,3,4,5,6) #return minimum
- m=min(tuple1) #print min element
- print("minimum element:",m)
Output-
4) tuple(seq)
This method converts the sequence into the tuple.
Syntax-
tuple(seq)
Example-
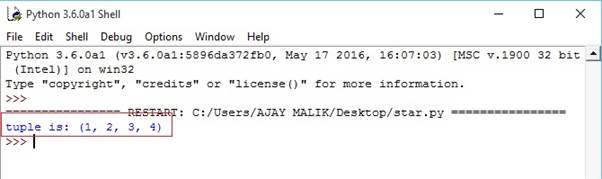
- seq=(1,2,3,4) #convert tuple in list.
- tuple1=tuple(seq) #print tuple
- print("tuple is:",tuple1)
Output-
Summary
In this article, you learnt some concepts of Python tuple like how to create a tuple, accessing a tuple element, insertion of element into tuple, deleting the element and you also friendly with some predefined function.