Python List
Introduction
In this article, you will learn about Python list, which is a data type. Every programming language supports the basic data structure as a sequence and to store the data in a sequence or to store the co-related data as a sequence.
Python supports six built-in sequences but most common are list and tuple.
Python also has built in functions for the manipulation and to perform an operation on the list.
Python list
List is versatile data type of Python. List can support any data type element in the same list. Python list element is separated by comma(,).
Syntax of list
List_name=[list_element]
Example
list1=[“c#corner”,1998]
Accessing value from the list
To access an individual value, list must use square brackets with an index for slicing an individual value.
Example
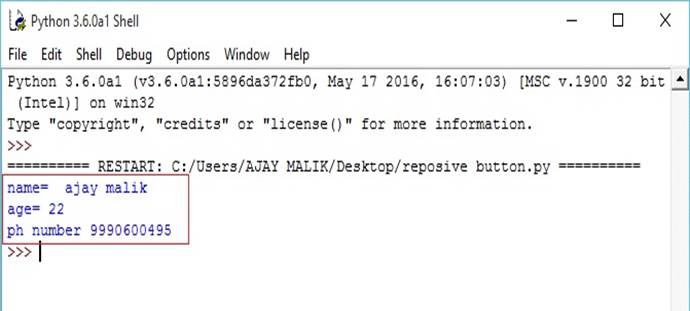
- list1["ajay malik",22,9990600495] #list with the name number and ph number
- print("name= ",list1[0]) #prints first element form list
- print("age=",list1[1]) #prints second element form list
- print("ph number",list1[2]) #prints third element form list
Output
Updating list in Python
In Python programming language, we can update the list, using index of the list to update the single element of the list or multiple elements of the list.
Example
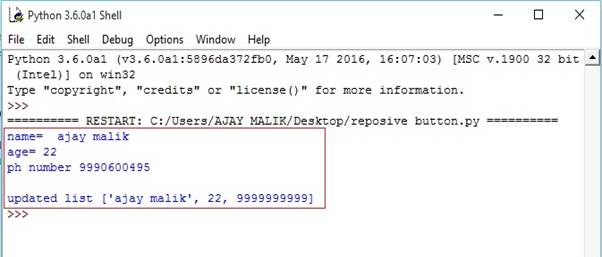
- list1=["ajay malik",22,9990600495] #list with the name number and ph number
- print("name= ",list1[0]) #prints first element form list
- print("age=",list1[1]) #prints second element fot list
- print("ph number",list1[2]) #prints third element from list#updating ph number in list
- list1[2]=9999999999#print updated list
- print("\nupdated list",list1)
Output
Deleting list element

Deleting list element
Python has del function, which is used to delete an individual element or whole list.
Example
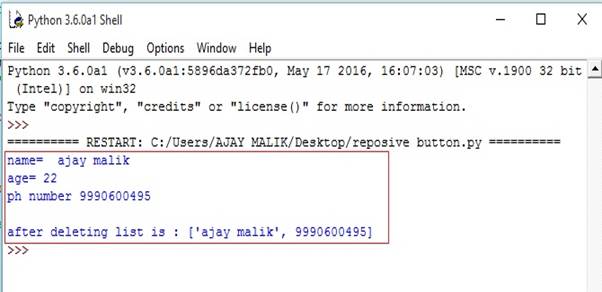
- list1["ajay malik",22,9990600495] #list with the name number and ph number
- print("name= ",list1[0]) #prints first element form list
- print("age=",list1[1]) #prints second element fot list
- print("ph number",list1[2]) #prints third element from list #deleting age from list
- del list1[1] #print list after delete element
- print("\nafter deleting list is :",list1)
Output
List operations

List operations
Python list is almost similar to string but the list is slightly different. Most common operations are listed below.
list1=[1,2,3] and list2[4,5,6]
| Operation | Expression | Result |
| Membership | 3 in list1 | True |
| Length | len(list1) | 3 |
| +(concatenation) | List1+list2 | [1,2,3,4,5,6] |
| Iteration |
For item in list1:
print(item)
|
123 |
Indexing, slicing and matrixes
Indexing, slicing and matrixes works similar to the string.
list1=[‘hello’,’Hello’,’HELLO’]
| Expression | Result | Description |
| list1[1] | Hello | Item at index 1 start from 0 |
| list[-1] | Hello | Count from right |
| list1[1:] | [‘Hello’,’HELLO’] | Start from 1 to end |
Built-in list function are given below,
1) len(list1)
It counts the length of list and returns the number of element in the list.
Syntax len(list)
Return value
It returns a number or length of the list.
Example
It returns a number or length of the list.
Example
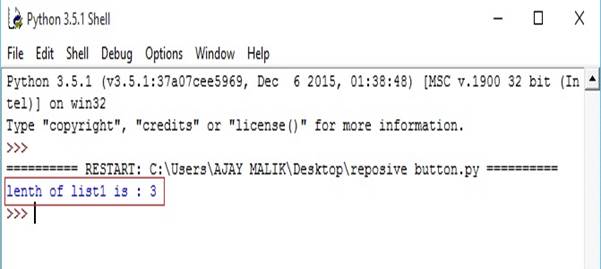
- list1=[1,2,3]
- list2=[4,5,6]
- n=len(list1)
- print("lenth of list1 is :",n)
Output

2) max(list)
It finds the maximum value in the list and returns the maximum value.
It finds the maximum value in the list and returns the maximum value.
Syntax
max(list)
return value
It returns the maximum value from the list.
Example
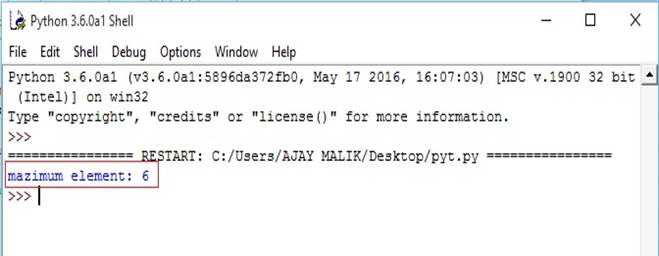
- list1=[1,2,3,4,5,6]#return maximum
- m=max(list1)#print max element
- print("mazimum element:",m)
Output
3) min(list)

3) min(list)
It finds the minimum value element and returns minimum value element.
Syntax
min(list)
return value
It returns the minimum value element.
Example
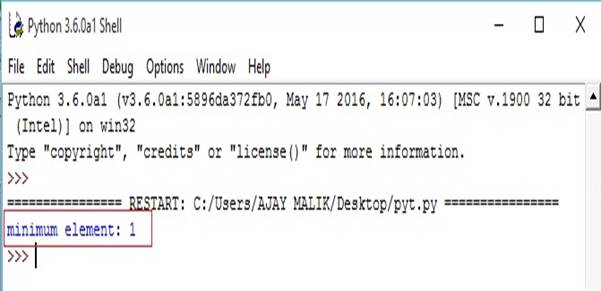
- list1=[1,2,3,4,5,6]#return minimum
- m=min(list1)#print min element
- print("minimum element:",m)
Output
4) list(seq)
This method converts a sequence into the list.
Syntax
list(seq)
Example
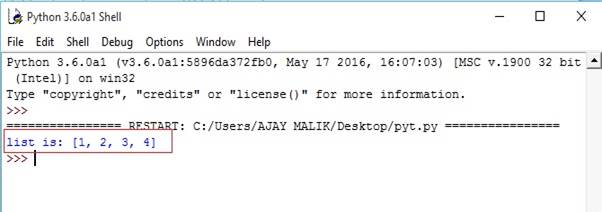
- seq=(1,2,3,4)#convert tuple in list.
- list1=list(seq)#print list
- print("list is:",list1)
Output

Python list method
list.append(obj)
It adds obj to the list (add value at the last of list). Only single value appends
Syntax
List.append(obj)
Return
This method can’t return any value.
Example
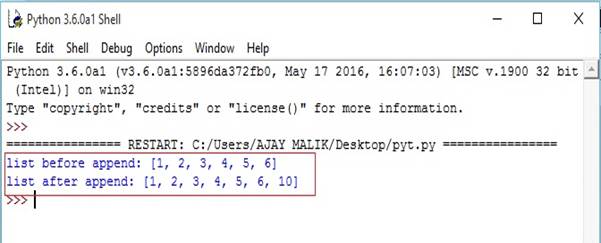
- list1=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
- print("list before append:",list1)#append list
- list1.append(10)
- print("list after append:",list1)
Output
list.count(obj)

list.count(obj)
It counts any obj in the list and returns how many times, an obj is occurred in the list.
Syntax
list.count(obj)
return It returns number of how many times obj occurred in the list.
Example
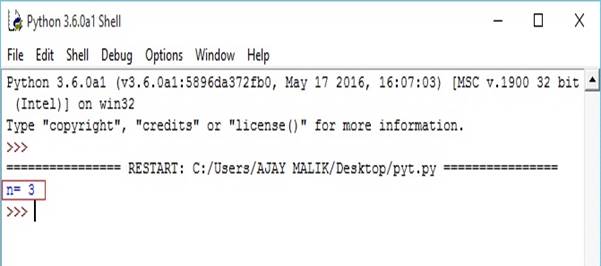
- list1=[1,2,3,4,5,6,6,6]
- n=list1.count(6)
- print("n=",n)
Output
List.extend(seq)

List.extend(seq)
Append seq to list
Syntax
List.extend(seq)
Return This method cant return any value.
Example
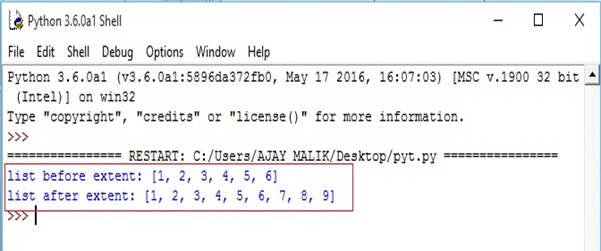
- list1=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
- seq=(7,8,9)
- print("list before extent:",list1) #append sequence in to list
- list1.extend(seq)
- print("list after extent:",list1)
Output
List.index(obj)

List.index(obj)
Returns index value of an obj in the list.
Syntax
list.index(obj)
Return value
Number or index value
Example
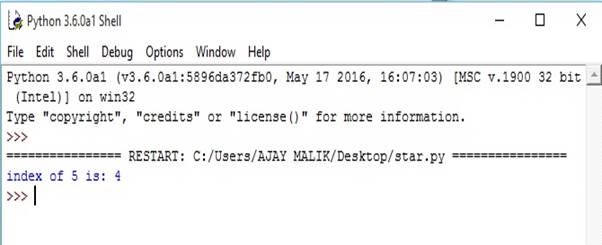
- list1=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
- print("index of 5 is:",list1.index(5))
Output
list.insert(index,obj)
Insert object at given index in the list.
Syntax
list.insert(index,obj)
Return
no return value
Example
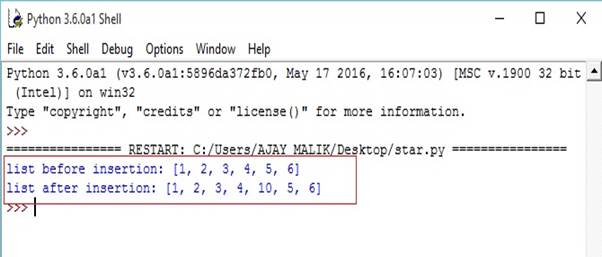
- list1=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
- print("list before insertion:",list1)#insertion
- list1.insert(4,10)
- print("list after insertion:",list1)
Output
list.pop(obj=list[-1])

list.pop(obj=list[-1])
It removes the last element and return that element.
Syntax
list.pop()
Example
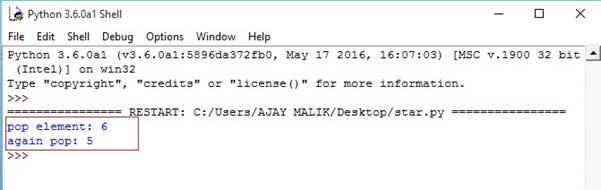
- list1=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
- print("pop element:",list1.pop())
- print("again pop:",list1.pop())
Output
list.remove()

list.remove()
It removes object from the list.
Syntax
List.remove(obj)
Return no return value.
Example
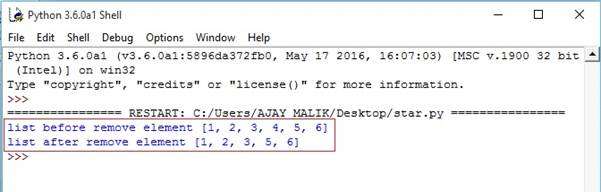
- list1=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
- print("list before remove element",list1)#remove element from list
- list1.remove(4)
- print("list after remove element",list1)
Output
list.reverse()
It reverses all the elements in the list
Syntax
list.reverse()
return no return value
Example
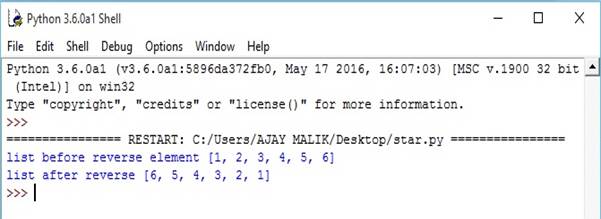
- list1=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
- print("list before reverse element",list1) #reverse function
- list1.reverse()
- print("list after reverse",list1)
Output

list.sort()
This function is used to sort the list element.
Syntax
List.sort()
Example
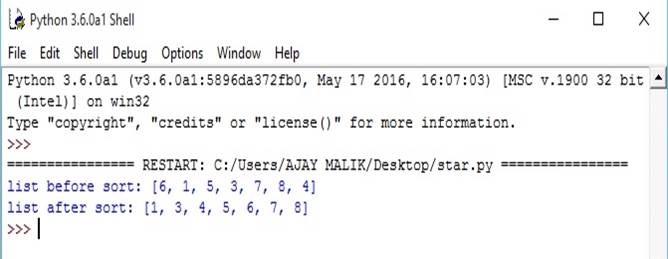
- list1=[6,1,5,3,7,8,4]
- print("list before sort:",list1) #sort list
- list1.sort()
- print("list after sort:",list1)
Output

Summary
In this chapter, you learnt some concepts of Python list like how to create a list , accessing list element, insertion of element into list ,deleting element and you also friendly with predefined function.