Continue Statement In Java
Continue Statement
Continue statement is sometimes required to skip some part of the loop and to continue the execution with next loop iteration. Continue statement is mainly used inside the loop helps to bypass the section of a loop and pass the control to the start of the loop to continue the execution with the next loop iteration.
Syntax
continue;
Let’s understand with the flowchart, given below.
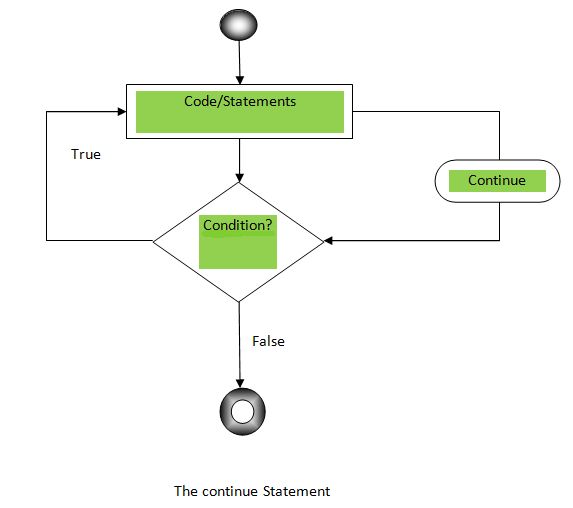

Let’s see an example of continue statement, given below.
Code

- public class ContinueExm {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int i;
- for (i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
- if ((i % 5) == 0) {
- continue;
- }
- System.out.println(i);
- }
- }
- }

Output
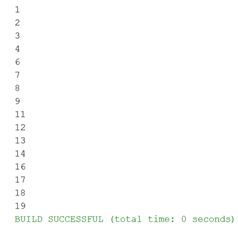

Here, the print statement is bypassed each time when the value stored in (i) is divisible by 5.
Continue statement with nested loop
Continue nested loop is used only if continue statement is used inside the nested loop.
For example
Code
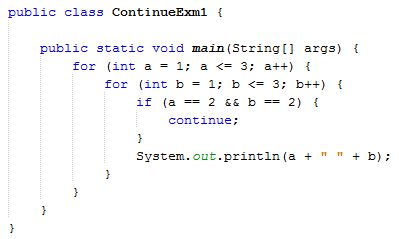
- public class ContinueExm1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- for (int a = 1; a <= 3; a++) {
- for (int b = 1; b <= 3; b++) {
- if (a == 2 && b == 2) {
- continue;
- }
- System.out.println(a + " " + b);
- }
- }
- }
- }

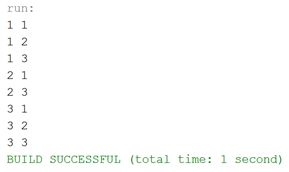
Output

Summary
Thus, we learnt continue statement is sometimes required to skip some part of the loop and to continue the execution with next loop iteration and also learnt how to use it in Java.